R Effect Size Interpretation
The guidelines he gives for r are for Pearsons r and cant be directly translated to the r for a rank-based test like the. 010 - 03 small effect 030 - 05 moderate effect and 05 large effect.

How To Interpret Effect Sizes In Psychology Statistics Next To Correlation It Should Say Pearson S R Data Science Psychology School Survival
The effect size gives the probability that a person picked at random from the treatment group will have a higher score than a person picked at random from the control group.

R effect size interpretation. 1998 chin1998 R2 019 - Very weak. A value closer to -1 or 1 indicates a higher effect size. Interpretation of effect sizes necessarily varies by discipline and the expectations of the experiment but for behavioral studies the guidelines proposed by Cohen 1988 are sometimes followed.
An absolute value of r around 03 is considered a medium effect size. For PLS SEM R-Squared of latent variables. First Westfall et al.
In the case of paired data this is a measure of the proportion of variance shared by the two variables and varies from 0 to 1. The effect size is used in power analysis to determine sample size for future studies. Small 10 medium 30 large 50.
Here a go-to summary about statistical test carried out and the returned effect size for each function is provided. 033. The interpretation values for r commonly in published litterature and on the internet are.
Effect size for mean differences of groups with unequal sample size within a pre-post-control design. Although a small d 20 is equivalent to a small r 10 the r equivalent of a medium-sized d 05 would be rated a small effect 24 not 30 in the correlational metric. One of the most famous interpretation grids was proposed by Cohen 1988 for a series of widely used indices such as the correlation r r 20 small.
The criteria for a small or large effect size may also depend on whats commonly found research in your particular field so be sure to. 2014 for the effect size calculation. The following guidelines are based on the literature values and my personal intuition.
An absolute value of r greater than 5 is considered to be a large effect size. The r value varies from 0 to close to 1. A related effect size is r2 the coefficient of determination also referred to as R2 or r-squared calculated as the square of the Pearson correlation r.
Thus Cohen requires larger effects when measuring the strength of association. Cohen 1988 provides some generalized interpretation for effect sizes. Intervention studies usually compare the development of at least two groups in general an experimental group and a control group.
R2 067 - Substantial. Small 20 medium 50 large 80. 019.
2014 showed how you can calculate the effect size. If you add more groups you will have higher 2 For a one-way ANOVA we could adjust 2 as follows2 SSB dfBSSWdfW SST SSWdfW where SSB and SSW are the SS Between and Within groups. R2 075 - Substantial.
R 40 moderate and r 60 large or the standardized difference Cohens d. The effect size is the same only rho spearman is used when the data does not meet a proper normality. Heres a link to an article that talks.
The strength of the effect size is the same as that for the r values with a weak effect size 03 or 03 a moderate effect size 03 to 05 or 03 to 05 and a strong effect size 05 or. Just to be clear r 2 is a measure of effect size just as r is a measure of effect size. Cohens d can be converted CL using the following formula Ruscio 2008.
This can be seen by looking at the table below. According to Cohen an effect size equivalent to r 25 would qualify as small in size because its bigger than the minimum threshold of 10 but smaller than the cut-off of 30 required for a. An absolute value of r around 01 is considered a low effect size.
025. 050. The paper suggested by simone Brysbaert and Stevens as the title indicates is focused on Power Analysis and Effect Size in Mixed Effects Models but it includes a calculation of effect size which is not present in simones answer with a reference to Westfall et al.
However the definition of a strong correlation can vary from one field to the next. According to Cohen 1988 1992 the effect size is low if the value of r varies around 01 medium if r varies around 03 and large if r varies more than 05. The value of the effect size of Pearson r correlation varies between -1 a perfect negative correlation to 1 a perfect positive correlation.
So for example if you want to know more about how. Effect Sizes Correlation Effect Size Family Adjusted ANOVA Coefficient of Determination 2 Note that 2 suffers from the same over-fitting issues as R2. 2011 hair2011 R2 025 - Very weak.
R is just a more commonly used effect size measure used in meta-analyses and the like to summarise strength of bivariate relationship. This should be useful if one needs to find out more information about how an argument is resolved in the underlying package or if one wishes to browse the source code. For Pearsons r the closer the value is to 0 the smaller the effect size.
Hi Alvaro - yes they are interpreted in the same way.

What Does Effect Size Tell You Simply Psychology

The Methods For Conducting And Interpreting Sample Size Calculations Are Available For Chi Square Mann Whitney U Independe Chi Square Research Studies Sample
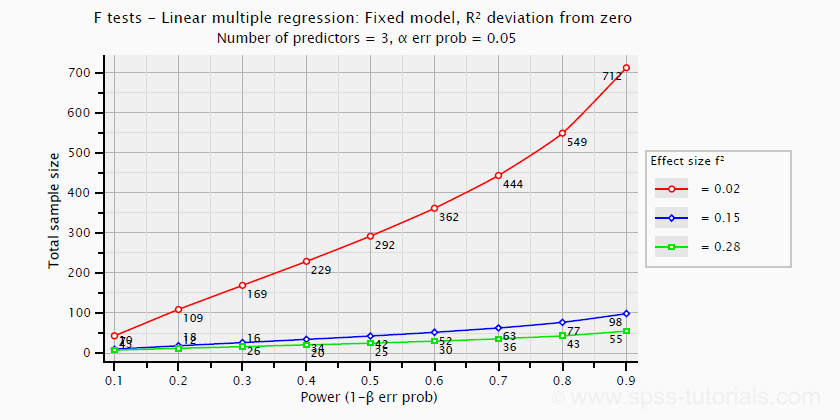
Effect Size In Statistics The Ultimate Guide
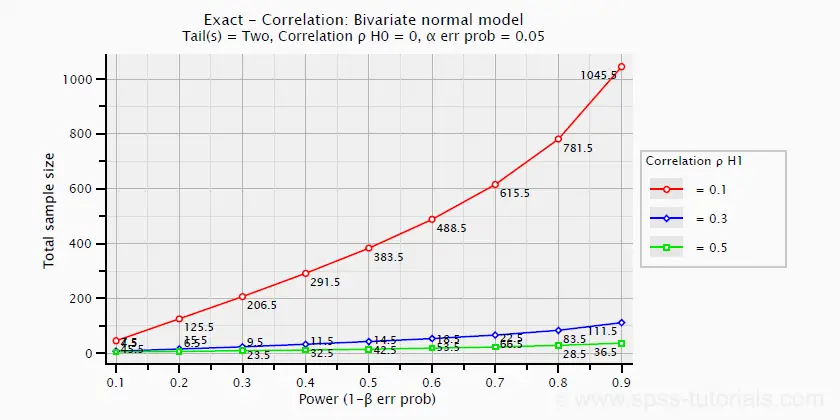
Effect Size In Statistics The Ultimate Guide

Interpreting Cohen S D Effect Size Predictive Analytics Visualisation Academic Research
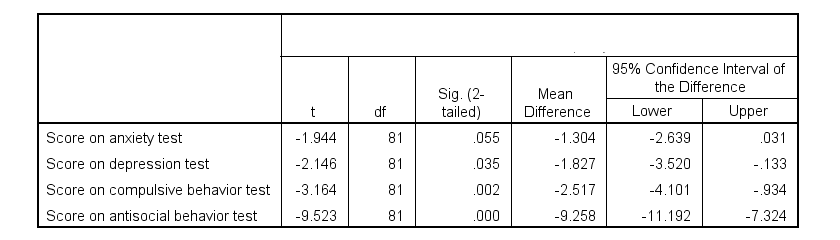
Cohen S D Effect Size For T Test
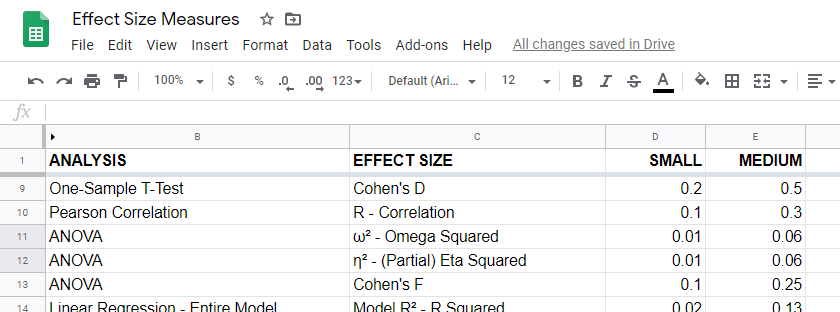
Effect Size In Statistics The Ultimate Guide

What Does Effect Size Tell You Simply Psychology
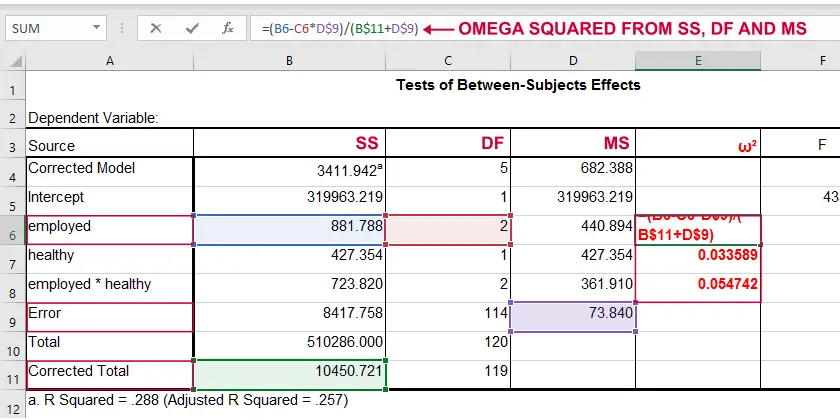
Effect Size In Statistics The Ultimate Guide

What Does Effect Size Tell You Simply Psychology
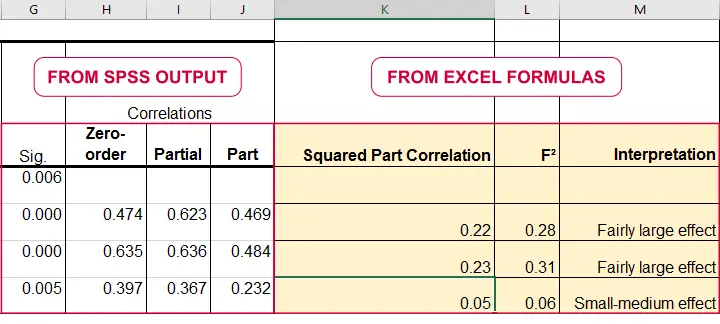
Effect Size In Statistics The Ultimate Guide
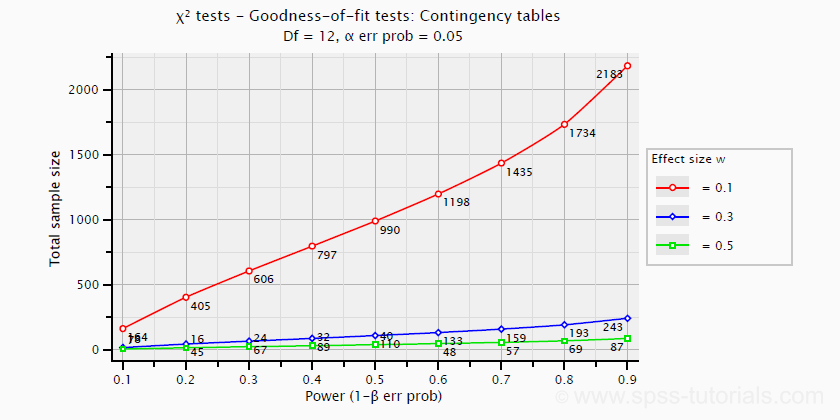
Effect Size In Statistics The Ultimate Guide

Posting Komentar untuk "R Effect Size Interpretation"