Effective Nuclear Charge Of Sodium
Z effective of sodium atom 11 88 22. These outermost electrons are also called valence or orbital electrons.

According To Slater S Rule Order Of Effective Nuclear Charge For Last Electron In Case Of Li Na And K 1 Li Na K 2 K Na Li 3 Na Li K 4 Li Na K
Therefore by using Slaters rule shielding constant and effective nuclear charge for 3s-electron of sodium atom σ.

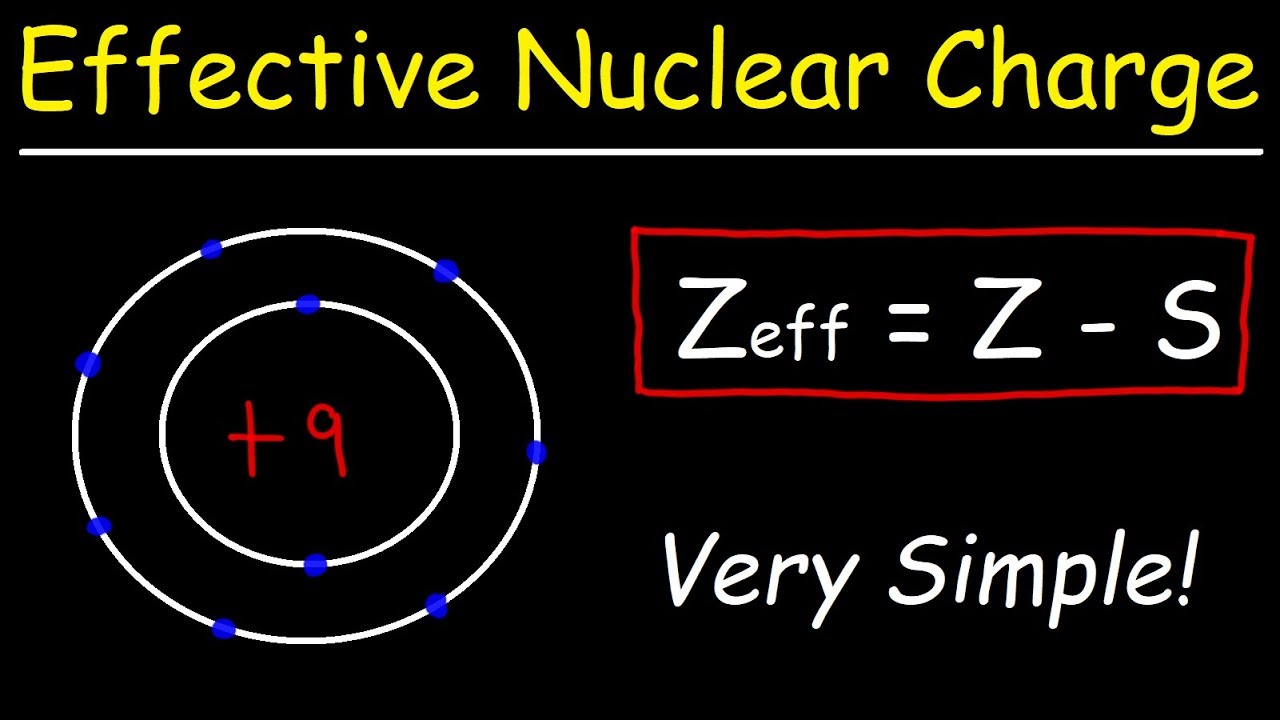
Effective nuclear charge of sodium. Zeff the effective nuclear charge. Question How to calculate the effective nuclear charge of the hydrogen atom. Thus effective nuclear charge 11 - 10 1.
For calculating the value shielding constant of inner electrons of the sodium atom the electron configuration according to Slaters rule 1s 2 2s 2p 8 3s 1. The effective nuclear charge experienced by valence electron of sodium is 220. In the table above we see the effective nuclear charge increases as we proceed from sodium to argon.
Besides the formula for calculating the effective nuclear charge of a single electron is as follows. In the case of the alkali metals Z eff increases from 13 for lithium to 25 for sodium to 35 for potassium. Even though sodiums nuclear charge is 11 and that of Neon is 10 however due to the distance from the nucleus the nuclear charge effect is very minimal in this case.
Screening Percentages Based on Slater Effective Nuclear Charge as a Versatile Tool for Teaching Periodic Trends Journal of Chemical Education volume. Effective nuclear charge Z Z σ Where Z Atomic number σ Shielding or screening constant. This article describes a relatively simple graphical procedure to calculate the effective nuclear charges experienced by the sodium valence electron from its atomic spectrum.
The electron removed from sodium is being removed from a higher energy level n3 than that of Neon n2. The effective nuclear charge experienced by the valence electrons is calculated by subtracting the number of inner core electrons from the nuclear charge on the element. The term effective is used because the shielding effect of negatively charged electrons prevents higher orbital electrons from experiencing the.
C How do the effective nuclear charges of sodium and chlorine affect their relative atomic radii. The effective nuclear charge may be defined as the actual nuclear charge Z minus the screening effect caused by the electrons intervening between the nucleus and valence electron. The effective nuclear charge is always smaller than the actual nuclear charge.
Note the value is a charge and contains no units. Now put the variables in the formula to know the value of Zeff effective nuclear charge. The total number of electrons 11 the inner electrons 10.
Z denotes the number of protons existing in the nucleus. There are no other electrons to shield it from the nuclear charge of a single proton. In fact however effective nuclear charge increases slightly as we go down a column because the more diffuse core electron cloud is less able to screen the valence electrons from the nuclear charge.
The energy terms can also be determined. The term effective is used because the shielding effect of negatively charged electrons prevent higher orbitals from experiencing the full nuclear charge of the nucleus due to the repelling effect of inner layer. Z eff Z Z eff Z actual - the effect of electron repulsions Z S where S is a screening constant and can be estimated by using the number of core electrons Real Sodium Atom Hypothetical Sodium atom By our method of estimation the Sodium Z eff.
The effective nuclear charge is the actual amount of positive nuclear charge experienced by an electron in a polyelectronic atom. Shielding constant 0 Zeff 10 0 10. Effective Nuclear Charge Formula.
More precisely it is the electric charge that the nucleus of a hypothetical atom would have capable of attracting its only electron with the same force with which the nucleus of the. The effective nuclear charge of the 3s1 electron in the sodium atom is 22. Effective nuclear charge refers to the positive charge felt or experienced by the outermost electrons in an atom that contains multiple electrons.
The sodium cation has the largest effective nuclear charge which results in electrons being held the tightest. The effective nuclear charge often symbolized as Z eff or Z is the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a multi-electron atom. A relation of Z with n for a given l is obtained and the Z values for all states of the valence electron are found.
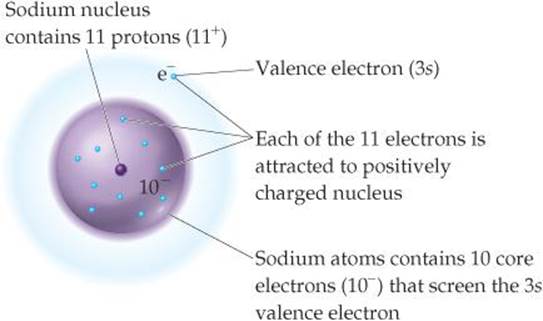
The effective nuclear charge represented as Z eff and in some cases as Z is the net nuclear charge that an electron experiences when it is in a polyelectronic atom that is it has more than one electron. Electron configuration of sodium Na 1s²2s²2p⁶ 3s¹. We therefore expect S to equal 10 and the 3s electron to experience an effective nuclear charge of Zeff 11 10 1 FIGURE 72.
In each of the above examples Ne F Na an atom has 10 electrons but the effective nuclear charge varies because each has a different atomic number. Answer 1 of 3. For example Us the Lithium atom then Z 3 atomic number and S 17.
Why are f orbitals bad at shielding. The nuclear charge is Z 11 and there aretrons 1s22s22p6. The configuration part of Na in bracket is known as the inner electrons while the ones without brackets are the outervalence electrons.
B What is the effective nuclear charge Zeff of Chlorine Cl. A What is the effective nuclear charge Zeff of Sodium Na. So the value of effective nuclear charge of 2s electron in Lithium atom is 13.
Effective nuclear charge Zeff is. Distance from nucleus. S average amount of.
If the electron is in s orbital it means it is nearest to nucleus and if in f shell it means it is farthest from nucleus. What is the Zeff of Na. Answer The hydrogen atom has a single 1S valence electron.
Zeff Z S. The charge is called effective because inner electrons with negative charge provide some sort of shield that. Sodium has the electron configuration Ne3s1.

How To Calculate Effective Nuclear Charge Slide Share

Mcat General Chemistry Ch 2 The Periodic Table Flashcards Quizlet
What Is Effective Nuclear Charge Of Chlorine Quora
Effective Nuclear Charge Periodic Properties Of The Elements Chemistry The Central Science

7 1 Development Of The Periodic Table Developed

The Shielding Effect And Effective Nuclear Charge Introduction To Chemistry

Calculation Of Effective Nuclear Charge Youtube
Property Trends In The Periodic Table The Layout Of The Periodic Table Is Organized Such That Various Physical And Chemical Properties Of The Elements Show Distinct Trends Or Patterns Knowing These Trends Helps One To Make Informed Decisions About The

Solved Nall Atom Has Electronic Configuration 152 252 2p6351 Chegg Com

According To Slater S Rule Effective Nuclear Charge Of Na Is X And Of K Is Y Respectively Youtube
How To Calculate The Effective Nuclear Charge Of An Electron Youtube

The Increasing Order Of Effective Nuclear Charge In Na Ai Mg And Si Atoms Youtube

Effective Nuclear Charge Electronic Structure Mcat Content

Posting Komentar untuk "Effective Nuclear Charge Of Sodium"