Effect Size Formula
This article describe the t-test effect sizeThe most commonly used measure of effect size for a t-test is the Cohens d Cohen 1998. The variations in the three formulas that you mention are due to differences in simplifications like nunu-2 approx 1 or nu n_1n_2-2 approx n_1n.

Photoelectric Effect Notations Einstein Physics
It is used f.

Effect size formula. According to Cohen 1988 1992 the effect size is low if the value of r varies around 01 medium if r varies around 03 and large if r varies more than 05. The criteria for a small or large effect size may also depend on whats commonly found research in your particular field so be sure to. A d of 1 indicates that the two group means differ by one standard deviation.
M 1 Mean of first observation. A value closer to -1 or 1 indicates a higher effect size. I found that Cohens guidelines for a medium effect size are almost spot 0n the.
Calculate the effect size correlation using the t value. But why not estimate the absolute effect size instead of cohens d which is a scaled effect size in this way and then compute cohens d based on this pooled absolute effect size. Cohens d 10 weak effect Cohens d 30 moderate effect Cohens d 50 strong effect.
In essence an effect size is the difference between two means eg treatment minus control divided by the standard deviation of the two conditions. Read more of two variables with the. F the Effect Size is a measure of the effect size.
Arithmetic mean where all the numbers are added and divided by their weight and in geometric mean we multiply the numbers together take the Nth root and subtract it with one. Effect Size Calculator for T-Test For the independent samples T-test Cohens d is determined by calculating the mean difference between your two groups and then dividing the result by the pooled standard deviation. There are primarily two ways.
Cohens d effect sizes should only be regarded as a guideline. Glass rank bi-serial correlation coefficient rg is the appropriate method of obtaining effect size for Mann-Whitney U test. The d statistic redefines the difference in means as the number of standard deviations that separates those means.
Where d Cohens index. Using this formula the effect size is easy to interpret. S 1 Standard deviation of first observation.
A d of 2 means that the group means differ by two standard deviations. From the value d we can find the effect size coefficient from the following formula. If the two groups have the same n then the effect size is simply calculated by subtracting the means and dividing the result by the pooled standard deviationThe resulting effect size is called d Cohen and it represents the difference between the groups in terms of their common standard deviation.
η² the Effect Size is an effect size measure. D fracmboxmean 1 - mboxmean 2mboxstd dev. Use Cohens d to calculate the effect size correlation.
It is the division by the. Cohens d M 1 M 2 SD pooled. η² σm²σm²σ² where σm is the sample size weighted.
The formulae and interpretation for rg is given in the book of King. The formula looks like this Navarro 2015. The standardized mean difference d To calculate the standardized mean difference between two groups subtract the mean of one group from the other M 1 M 2 and divide the result by the standard deviation SD of the population from which the groups were sampled.
The effect size is calculated by dividing the difference between the mean Mean Mean refers to the mathematical average calculated for two or more values. R d d2 4 r d d 2 4. Where d Cohens d Value Standardized Mean Difference M1M2 Mean Values of the First and Second Dataset SD1SD2 Standard Deviation of the First and Second Dataset r Effect Size.
F σm σ where σm is the sample size weighted standard deviation of the means and σ is the standard deviation within a group. For Pearsons r the closer the value is to 0 the smaller the effect size. The value of the effect size of Pearson r correlation varies between -1 a perfect negative correlation to 1 a perfect positive correlation.
For calculating the effect for pre-post comparisons in single groups. The effect size correlation was computed by SPSS as the correlation between the iv TREATGRP and the dv SUDS4 r Yl. M 2 Mean of second observation.
A histogram of 297 HRV effect sizes from case-control studies with the 25th 50th and 75th percentile shown. Effect sizes should be examined within the research context and information from similar studiesinterventions may facilitate this evaluation. A d of 25 indicates that the two means differ by 25 standard deviations and so on.
Normal bell curve shape. Effect Size ES Average of the post-test scores Average of the pre-test scores Average standard deviation The average standard deviation in the above formula refers to the standard deviation for the pre-test and. Ellis Hong Kong Polytechnic University.
2 Cohens d follows a classification system based on their effect sizes Cohen 1992 ie.

Brandi S Buzzar Blog Physical Principles The Effect Of Hail Size On Damage Physics Principles Hail
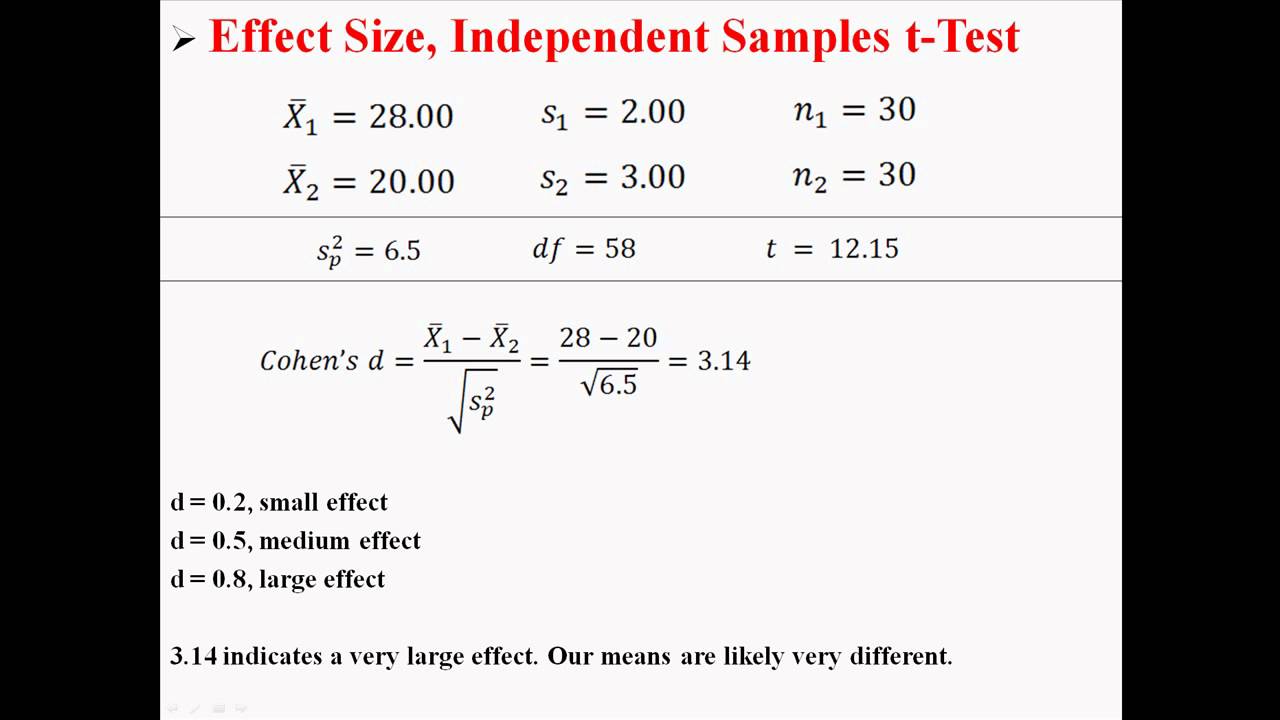
Pin On Lean Six Sigma And Statistics

Mk Botanical Effects Hydrate Moisturizer Dry Skin Moisturizer For Dry Skin Moisturizer Dry Skin

The Goal Of Six Sigma Is To Improve Your Processes Like How To Fix Variation And Products And Increase E Lean Six Sigma Business Management Business Analysis

Pin On Skin Body Care Emails Web Design

Client Chose Advancing Latino Health As Tagline Math Web Development Clients

Photoelectric Effect Physics And Mathematics Physics Physics Concepts

Z Or Standard Score Value Calculator Standard Deviation Psychology Notes Statistics Math

Doodle Math Algebra And Geometry School Equation And Graphs Hand Drawn Physics Science Formulas Vector Image Formula In 2021 Free Math Lessons Science Formulas Math

Adamjee Coaching Trigonometry Definitions And Formulae Mathematics 10th In 2021 Trigonometry Mathematics Math Formulas

Pin By Bouret On Maths Math Methods Learning Mathematics Algebra Formulas

Photoelectric Effect Notations Einstein Physics


Posting Komentar untuk "Effect Size Formula"